Guide On The Use Of Mouthwash
Mouthwashes are a complement to brushing, but they can never replace it. If you use this oral hygiene supplement together with dental floss, you will contribute to maintaining a healthy mouth.
It may be thought that only using mouthwash after meals can prevent the accumulation of plaque and the appearance of cavities, however this is not the case. To choose the right mouthwash for your needs, ask for advice from oral health professionals. They will indicate the appropriate one in each case and the correct way of use.
Mouthwash with alcohol or without alcohol
When choosing a mouthwash you can take into account its alcohol content. In addition to its antiseptic action, in many cases it is necessary to dilute some of its components.
If it contains alcohol, you should not swallow it or use it continuously. In the long run, the use of mouthwashes with alcohol can affect the oral mucosa. However, there are alcohol-free alternatives in the oral health market.
Some mouthwashes contain CPC – cetylpyridine chloride – which is safe and effective. It is an ingredient that helps prevent the accumulation of germs.

Types of mouthwashes
Mouthwashes are divided into two large groups: those for daily use and those for treatment. Those for treatment are indicated to solve problems such as inflammation of the gums, tooth sensitivity or mouth sores, among others.
In general, mouthwashes should be used half an hour after brushing, as the components of the pastes can interfere with their effectiveness. Here are the indications for the most commonly used mouthwashes.
Halitosis or bad breath
If you suffer from halitosis, the most important thing is to know the cause. Although it is usually the result of the putrefaction of bacteria when food remains in the mouth. Mouthwashes to treat bad breath contain ingredients such as hydrogen peroxide, zinc, chlorhexidine or triclosan.
It is recommended to rinse with 15 ml of undiluted mouthwash, for 30 seconds, at least 2 times a day or after each brushing. For greater effectiveness, try not to rinse with water, or eat or drink immediately after use.
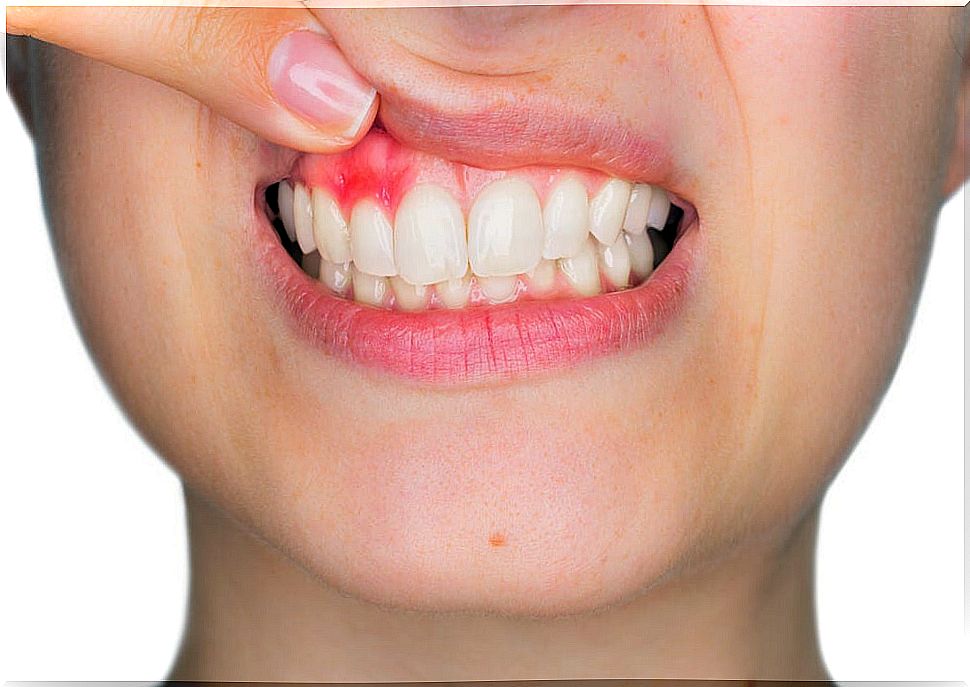
Gum conditions
These problems appear when bacteria from dental plaque build up on the gums and lead to inflammation and bleeding. They can cause the loss of part of the bone and even the tooth.
For the treatment of the gums, soft mouthwashes, without alcohol, are usually recommended. They incorporate ingredients such as povidone iodine, phenols or essential oils in their formula. Mouthwashes with metal salts are also indicated for these cases.
To treat periodontitis, chlorhexidine, which is a broad-spectrum antiseptic effective against bacterial plaque , is also indicated.
Mouthwash for cavities
Cavities are one of the most common oral problems that can be avoided with proper oral hygiene and fluoridation treatment. Fluoridation helps keep the tooth surface intact and prevents it from becoming porous, obstructing the entry of bacteria.
Mouthwashes that contain fluoride in their composition are of great help, since what is sought is to reinforce tooth enamel.
Xerostomia or dry mouth
If you have a tendency to dry mouth due to having little saliva, you have a higher risk of developing bacterial infections, since saliva is not fulfilling its protective function. For this reason, the use of a suitable mouthwash that, in addition to refreshing, acts as a preventive measure, is recommended. This type of mouthwash is rich in mineral salts, vitamin E and fluoride.
Orthodontics
If you wear orthodontics, it is necessary to use mouthwashes because brushing in these cases is not enough. With the use of the mouthwash, you reach the hard-to-reach areas when brushing, thus ensuring comprehensive mouth care.
Rinse with 15 ml of undiluted mouthwash for 30 seconds, at least 2 times a day, or after each brushing.
Conclution
The use of mouthwash removes food debris in the places where the brush cannot reach. Therefore, in addition to refreshing the breath, they help maintain proper oral health.
Similarly, there are precise indications for a therapeutic use of mouthwashes. They are specific cases in which a dental professional can guide you to choose the right one.