Tachycardia In Children, How To Detect It?
Tachycardia in children is a condition that greatly scares parents. Often, it is suspected that after the symptom there is a serious pathology; Fortunately, this is not the right thing to do in all cases.
Even so, as we will see in this article, consultation with a specialist is essential to clear up doubts. Through some simple complementary methods it is possible to determine the benignity or dangerousness of these altered beats.
When is there tachycardia in children?
Tachycardia is the increase in heart rate above the values considered normal for each age. These normality figures are established based on an average of the populations, that is, studying what is the most common frequency among healthy individuals.
For the general population, it is considered normal for the heart to beat between 60 and 100 times in one minute. Below that amount it is a bradycardia and above it is a tachycardia.
However, in children it is necessary to take certain precautions, because their normal frequencies are somewhat different and they are modified as they advance in age, until they reach the values of adults.
In a baby younger than 6 months, there is no abnormality up to 180 beats per minute. Then, up to age 10, the heart can beat up to 140 times in the same time without signifying tachycardia.
In adolescence, frequencies of up to 120 beats are considered common, which will be up to 100 in adulthood. There is no specific age at which the adult heartbeat begins, but the end of adolescence could be established, approximately between 16 and 18 years of age.
So, we will say that there is tachycardia in a child when the expected beats for his age are exceeded in one minute. As long as the detection is repetitive or constant, since momentary increases are to be expected when the little one exercises, for example.

What can be the causes of infantile tachycardia?
Tachycardias in children are classified within arrhythmias, which would be any alteration in the heart rhythm. When the rate falls it is a bradyarrhythmia and when it accelerates a tachyarrhythmia.
In general, the causes of infantile tachycardia are 3: sinus in origin, due to electrical alteration or due to congenital hereditary malformations. The first is benign and does not need a specific treatment, unless the symptoms disturb daily life too much. The other two sometimes require corrective surgery.
Sinus tachycardia is a consistently higher than normal heart rate, with an electrocardiogram showing no electrical disturbances. Its origin is in the sinus node, which is an anatomical structure that commands the electrical impulse of the heart muscle.
States of anxiety, intense exercise and fever cause it. However, beyond these specific facts, there are children with a more hyperactive sinus node, which translates into a heart that always beats at high frequencies.
If there are no severe symptoms other than palpitations and a galloping sensation in the chest, they are not treated with drugs. His condition is explained to the child and he is taught to live with it.
On the other hand, among electrical alterations, a cause of tachycardia in children is the existence of an abnormal pathway. This means that the heartbeat impulse system, inside the heart, has a different wiring than normal.
Consequently, the muscle is stimulated by alternate pathways, accelerating the rate. If the site of the abnormality is accurately detected, radiofrequency ablation is sometimes performed to fix it.
In third and last place we have hereditary and congenital heart diseases, among which are channelopathies. They are more serious pathologies, with changes at the cellular level in families where parents and grandparents have had the same condition.
How is tachycardia detected and diagnosed in children?
The first sign of tachycardia is usually manifested by the little ones. A number of symptoms reveal that the heart is beating faster than expected. Classic sensations include the following:
- Chest pain.
- Shortness of breath.
- Cardiac gallop, like blows from the inside out.
- Anxiety or manifestations of fear.
The adult who is close to the child with these symptoms can quickly check the rate by taking the pulse. This is easy to do by placing two fingers in the canal of the radial artery, on the wrist, on the outer side. There the heartbeats are perceived and can be counted for a minute.
The acceleration perceived with the taking of the pulse is reason enough to carry out, later, a cardiology consultation. The doctor will indicate and perform an electrocardiogram test in the same office, which is the electrical recording of the heart’s activity on a paper designed for this purpose.
The EKG machine consists of a series of electrodes that are placed on the child’s limbs and chest. For a short time the device makes a thermosensitive needle move on a piece of paper, recording the heartbeat.
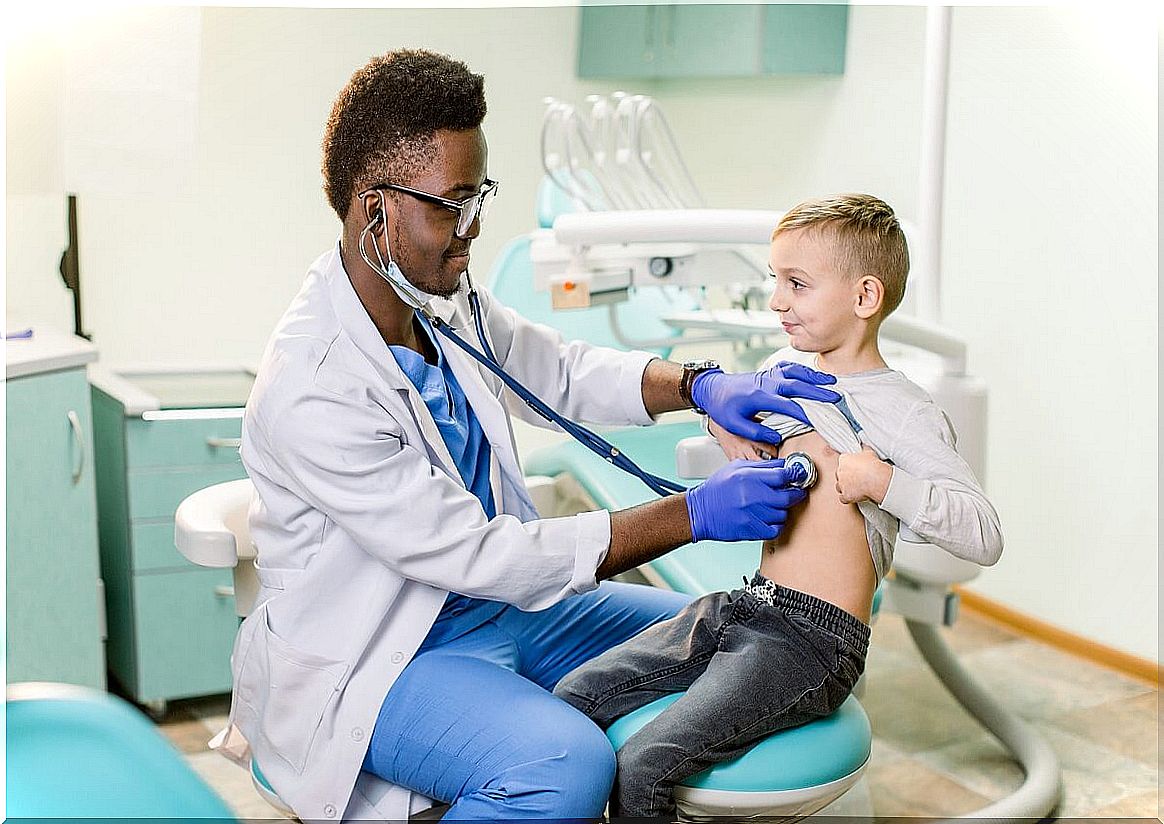
If there is a tachycardia, this complementary method will not only detect it, but will also reveal where it came from and what shape the heartbeat is. According to the initial result, other tests may be requested to improve and refine the diagnosis.
Sometimes an echocardiogram, chest X-ray, Holter monitor (if you are an adolescent), and blood tests are used if associated morbidities, such as anemia, are suspected.
Suspicion of channelopathy will lead the child and his parents to request a genetic panel to identify the DNA alteration that gave rise to the tachycardia. This is not frequent, but if an accurate diagnosis is not reached with the other methods, this option will surely be considered.
An almost always benign disorder
Tachycardia, in most children, is benign. It responds to a change in the sinus node that should not be treated. Although it always scares parents, we can be sure that it is more likely not to evolve to a complication.
However, its detection by an adult requires a cardiology consultation. The most serious causes should be ruled out and an EKG should be performed at a minimum. The doctor will know how to inform if only basic measures are taken or if a therapy with drugs or surgery is advanced.